選択した画像 aristocracy in ancient greece 600849-Conflict between aristocracy and peasantry in ancient greece
The term 'aristocracy' derives from the Greek and means literally kratos ('rule') of the aristoi ('the best') However, our ideas of what constitutes an aristocracy – images of feudal kings and their lords – are not wholly compatible with what aristocracies in the ancient world were actually like Aristotle, in his Politics, discussed four main types of government or 'constitutions' (monarchy, aristocracy, oligarchy, and democracy), and considers aristocracy largely aWhat is Aristocracy Aristocracy is derived from the Latin terms aristokratía meaning the rule of the best As its etymology suggests, the concept of aristocracy first appeared in ancient Greece, and it referred to the rule by the bestqualified citizensAristocracy as was used in ancient Greece worked as a sort of parliamentary democracy in which as small group of powerful and smart individuals fromed a senate to rule on matter o the state

What Is Aristocracy Aristocracy
Conflict between aristocracy and peasantry in ancient greece
Conflict between aristocracy and peasantry in ancient greece-At the time of the word's origins in ancient Greece, the Greeks conceived it as rule by the best qualified citizens—and often contrasted it favourably with monarchy, rule by an individual In later times, aristocracy was usually seen as rule by a privileged group, the aristocratic class, and has since been contrasted with democracyIn Ancient Greece, the aristocracy was a defining feature of the social fabric of the Greek polis and would be in constant competition with each other for wealth, power, and prestige, as well as



Greek Wh1 Project By Mkwarlick On Emaze
The concept of aristocracy originated from ancient Greek, where the Greeks empowered a council of leadingcitizens The council of citizens was the senate of any political unit in ancient Greece, including a citystate The Greeks were against the idea of a monarchy, and since their democratic government failed, they upheld aristocracyThe concept of aristocracy originated from ancient Greek, where the Greeks empowered a council of leadingcitizens The council of citizens was the senate of any political unit in ancient Greece, including a citystate The Greeks were against the idea of a monarchy, and since their democratic government failed, they upheld aristocracyIn Ancient Greece it was used to describe the rule of the most qualified or the best citizens It was used by philosophers such as Aristotle or Plato, described, as said, as the rule of the most qualified, system which was favorably compared with Monarchy, the rule of the one In this hypothetical Aristocratic system hereditary rule would be forbidden and would only be allowed in case the children of the former Aristocrats performed in a way worth giving them this role
The common Greek farmers kept animals like cows, sheep horses, and chicken;Etymology The term "aristocracy" ( Greek ἀριστοκρατία) was first used in Athens with reference to young citizens (the men of the ruling class) who led armies at the front line Due to martial bravery being highly regarded as a virtue in ancient Greece, it was assumed that the armies were being led by "the best"Ancient Greece Aristocracies have been used as a form of government since the earliest days of recorded history In Ancient Greece, a polis, or a Greek citystate, could be governed by a monarch,
The Athenian Aristocracy Before democracy, from the 8th to the 6th century BC, Athens was prosperous economically but no more significant than many other citystates in Greece Silver deposits south of Athens, quarries of fine white marble, and extensive clay beds that skilled potters used to good advantage made the city wealthy but otherwise unremarkableFacts about Aristocracy 3 the Greeks The concept of monarchy was not well accepted in ancient Greece because the government was ruled by a single individual When the democracy in the ancient Greece fell, people began to seek another form of government They chose aristocracy Find out ancient Greek government facts hereThe Archon (chief magistrate) Draco made severe reforms to the law code in 621 BC (hence " draconian "), but these failed to quell the conflict Eventually the moderate reforms of Solon (594 BC), improving the lot of the poor but firmly entrenching the aristocracy in power, gave Athens some stability



Ancient Greek Aristocracy Bing Images Greek Art Ancient Greece Ancient Warriors



Monarchy Aristocracy Tyranny Oligarchy And Democracy As Forms Of Government In Ancient Greek City States Steemit
In order to understand our governments, we need to understand the governing practices of ancient Greece, which would have been either monarchy, aristocracy, tyranny, oligarchy, or democracy Comparing Governments The best place to start to understand ancient Greece rulers is the aristocracy, simply because aristocracy can be found in allIntroduction Monarchy, aristocracy, tyranny, oligarchy and democracy were all forms of government found at different times and in different citystates in Ancient Greece Elements of more than one of these forms also coexisted, however, and the modern connotations of labels such as these are not necessarily the same as those that prevailed inOppressed individuals, while not engaged with political undertakings, were indispensable to the Athenian economy The nature of conflict between aristocracy and peasantry in ancient Greece How did this conflict culminate in the establishment of democracy Reviewed by myexamsolution on January 08, Rating 5



Aristocracy Definition Explanation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Ancient Greece Part Ii Government Youtube
In the preClassical period, ancient Greece was composed of small geographic units ruled by a local king Over time, groups of the leading aristocrats replaced the kings Greek aristocrats were powerful, hereditary noblemen and wealthy landowners whose interests were at odds with the majority of the populaceIn history, most ancient societies have thrived on quite a few paradoxes just like ancient Greece where citizens were taught to live freely But, at the same time slavery in ancient Greece was also a parallely thriving practice, or say industry The practice of keeping slaves was not uncommon in ancient Greece or RomeDifferent types of birds were favored as pets in ancient Greece The Mynah bird was quite common pet among the aristocracy and often received special care Parakeets were also kept
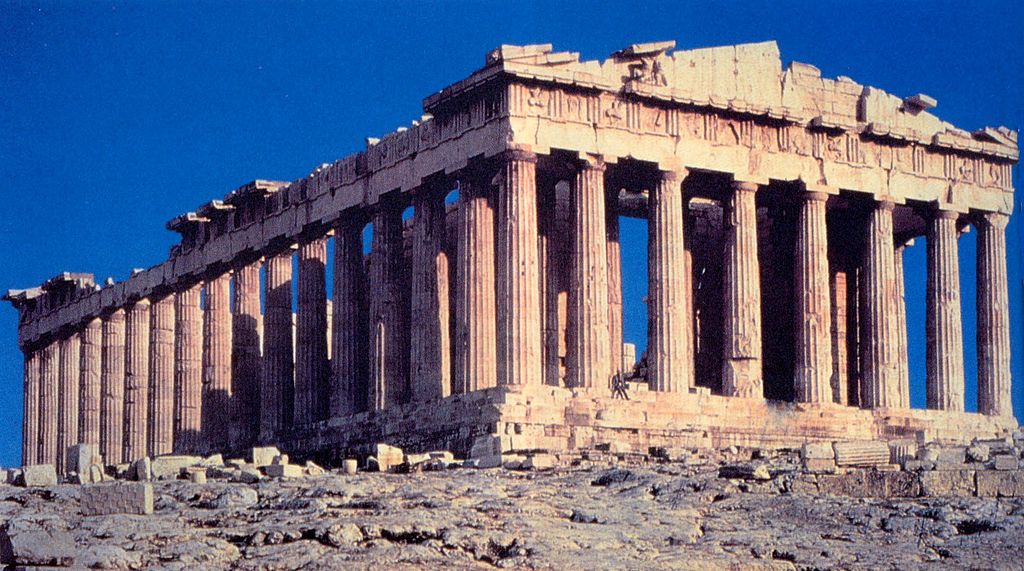



Brexit And The Parthenon Marbles Greece Areas Homepage Osservatorio Balcani E Caucaso Transeuropa


Redstateeclectic The Invention Of The Modern Public
The term aristocracy is a compound word stemming from the singular of aristoi, aristos (ἄριστος), and the Greek word for power, kratos (κράτος) From the ancient Greeks, the term passed to the European Middle Ages for a similar hereditary class of military leaders, often referred to as the nobility As in Greece, this was a class of privileged men and women whose familial connections to the regional armies allowed them to present themselves as the most "noble" or "best" of societyIn Ancient Greek, the word aristocracy means the rule of the best, but it has come to be linked with rule by Nobility There are different kinds of aristocracy with different ways the government is set up In history, most aristocracies are hereditary Members of the ruling group have passed on power to their eldest surviving son, and sometimes to their eldest daughterThe Ancient Greek term Aristocracy meant a system of government with "rule by the best" This is the first definition given in most dictionaries The official breakdown is from the Greek word "Aristo" meaning the "best" and "Kratia" is "to rule"



Related The Dexileos Stele A Study Of Aristocracy And Democracy In Greek Art Article Page 1 Ancient History Encyclopedia



The Use Of Aristocracy In Politics International Association For Political Science Students
(Four Forms of Government in Ancient Greece PDF, nd) According to Dictionarycom, an aristocracy is "a governing body composed of those considered to be the best or most able people in the state" In the great majority of ancient Greece citystates, there lied this rich aristocracy issueIn the Dark Ages an aristocracy ruled Greece Aristocracy means "rule of the best" People were born into the aristocracy, and these families controlled the polis at the early stages of the Archaic Period Then, gradually, farmers outside of the aristocracy gained control of family plots of land, and gained some wealthIn Ancient Greece, the aristocracy was a defining feature of the social fabric of the Greek polis and would be in constant competition with each other for wealth, power, and prestige, as well as



Ancient Greece 1 500 A D Chronology Heilbrunn Timeline Of Art History The Metropolitan Museum Of Art
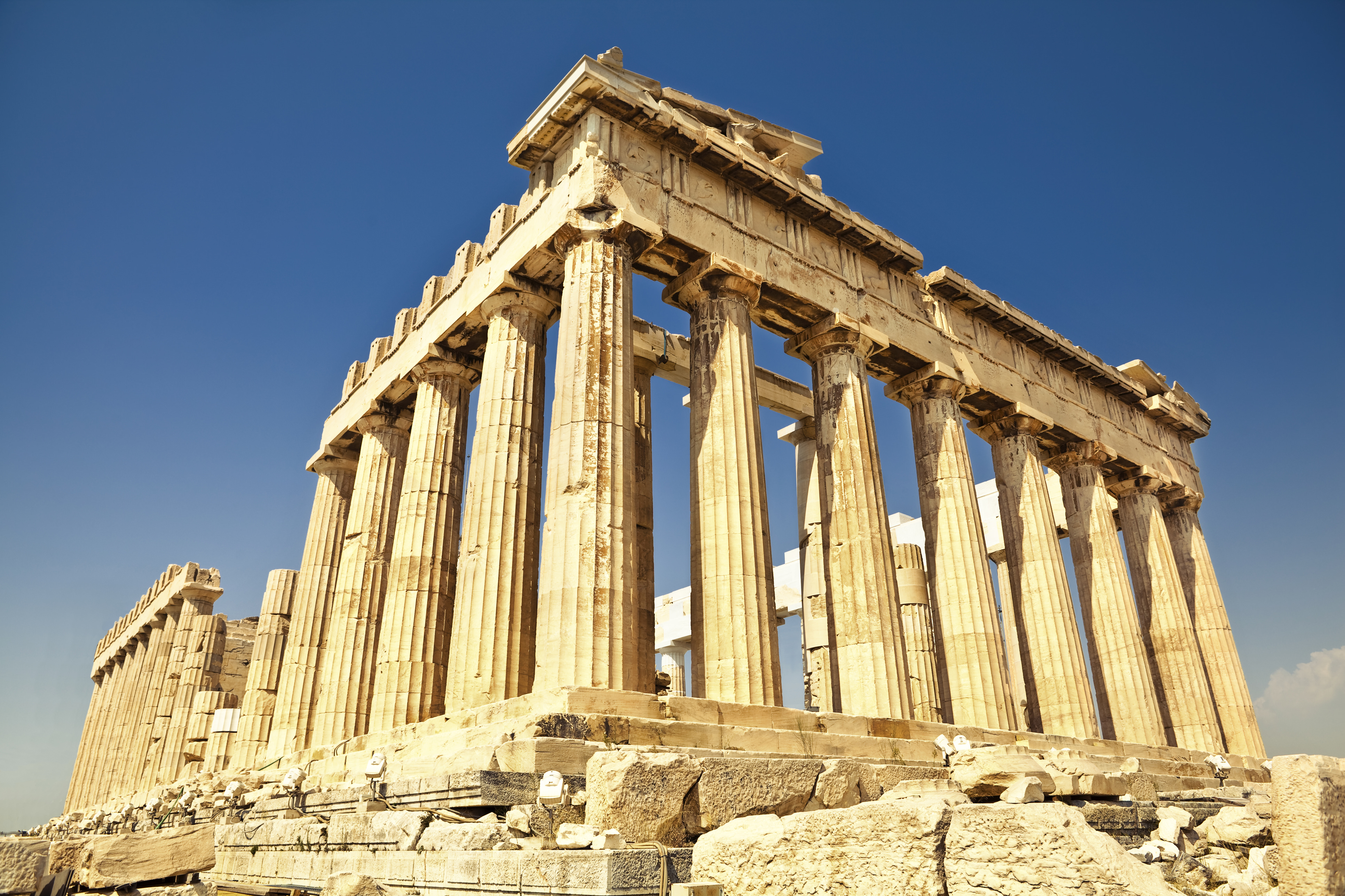



Eupatridae Nobility Of Attica In Ancient Greece
Introduction Monarchy, aristocracy, tyranny, oligarchy and democracy were all forms of government found at different times and in different citystates in Ancient Greece Elements of more than one of these forms also coexisted, however, and the modern connotations of labels such as these are not necessarily the same as those that prevailed in Ancient GreeceAristocracy is a Greek term meaning "rule of the best" It originated in ancient Greece, where a council of educated leading citizens ruled the rest of the uneducated populace The ancient Roman Republic and England in the 18th and 19th century followed a similar model of government, which was considered a viable alternative to an absolute monarchy or dictatorshipAristocracy is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats The term derives from the Greek aristokratia, meaning 'rule of the best' At the time of the word's origins in ancient Greece, the Greeks conceived it as rule by the bestqualified citizens—and often contrasted it favorably with monarchy, rule by an individual The term was first used by such ancient Greeks as Aristotle and Plato, who used it to describe a system


Education In Ancient Greece Facts And Details



Aristocracy Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
The term 'aristocracy' has been derived from the Greek word 'aristokratia', which is literally translated as 'rule of the best' This form of government originated in ancient Greece, where, apart from the political clans and top clergymen, the population was largely illiterate, making highlyqualified men desirableThe common Greek farmers kept animals like cows, sheep horses, and chicken;Aristocracy is a form of authority that assumes human equality is largely a myth Aristocracy is different from oligarchy In fact, in Aristotle's famous view, these two are polar opposites, having nothing in common Literally, from the Greek, "aristocracy" means "rule of the best," and puts ability above equality in searching for social justice



Aristocracy Archives Quatr Us Study Guides


Aristocrats Hold Greece Together The Greek Banner
The word ''aristocracy'' was first used in ancient Greece by Plato and Aristotle to describe a governing system where only the best few would be chosen as rulers The concept of aristocracy originated from ancient Greek, where the Greeks empowered a council of leadingcitizensCivil Society in Ancient Greece The Case of Athens by Roderick T Long Author's note as fortunes began to be accumulated by people in the lower ranks of the aristocracy, who now had the resources and influence to contemplate challenging the power of their superiors Second, it brought higher living standards to the common people, thusThe words 'aristocrats', 'aristocracy' and 'aristocratic values' appear in many a study of ancient history and culture Sometimes these terms are used with a precise meaning More often they are casual shorthand for 'upper class', 'ruling elite' and 'high standards' This book brings together



What Is An Aristocracy Worldatlas


Q Tbn And9gct6lrqkvyg Bjkhesx1e9f6cebgg7jpvgigrupubabyzjkvtsnc Usqp Cau
The physical geography of Greece encouraged the development of the polis because there were lots of mountains so the acropolis would be on the mountain and the city surrounded itAncient Greece was a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of antiquity This era was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and colonization of the Mediterranean Basin This was followed by the age of ClassicalAristocrats were the "upper class" citizens of Ancient Greece They replaced the monarchy in the polies of Greece They formed the cavalry and hoplites, Ancient Greek soldiers, to protect their city state The Aristocrats owned most of the land and ruled with a council Power within the Greek citystates was held by large aristocratic geni, or clans These aristocratic clans controlled large areas in Attica around Athens



The Honor Code Of The Greek Hero The Greek Honor Code
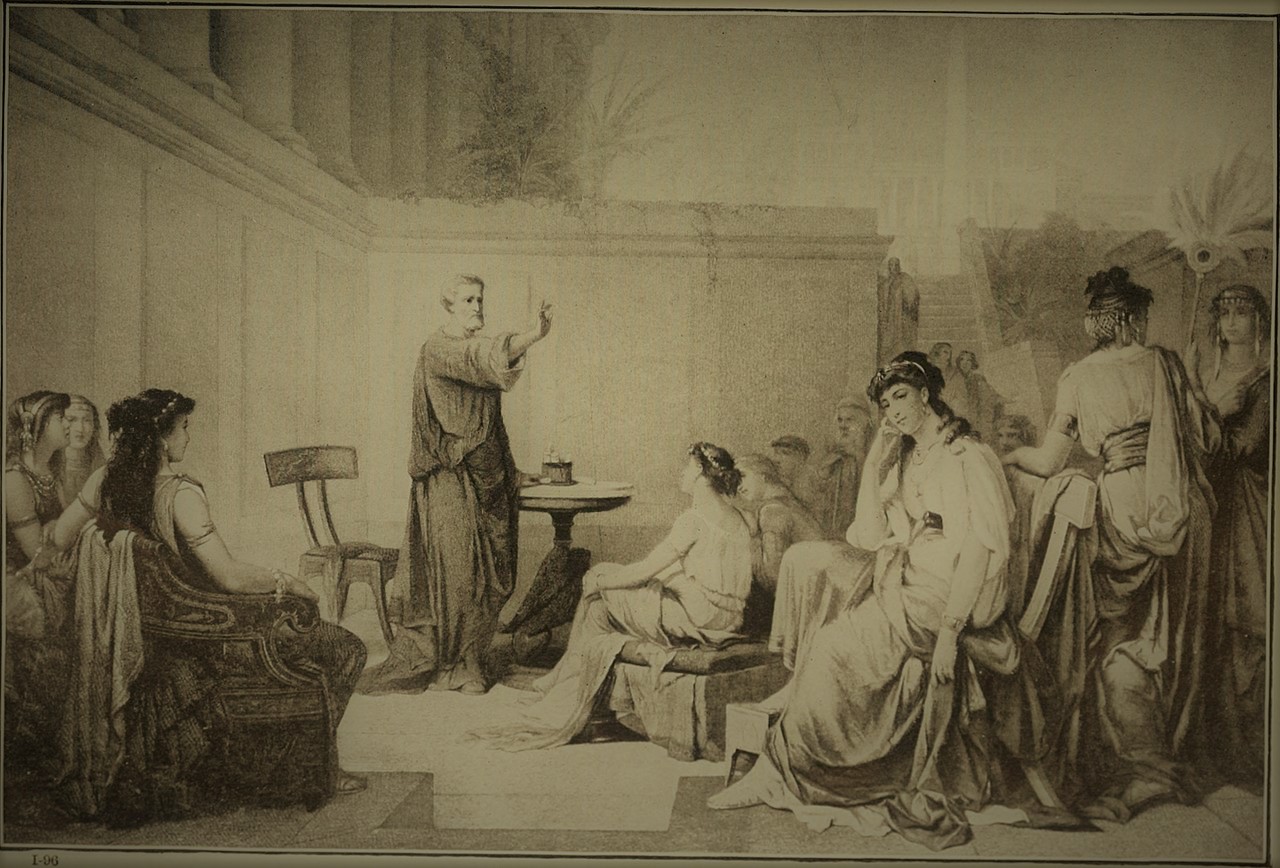



A History Of Oligarchy And Plutocracy Since Ancient Greece Brewminate
These systems excluded the whole citizen body of Ancient Greece and favoured the upper classes this triggered conflict amongst the two which in turn led to the creation of democracy There were three major forms of government employed in Ancient Greece, these are monarchy, tyranny and oligarchy (Ancient Athens, 10)Aristocracy comes from Aristokratia, a Greek word meaning rule of the best This is why both Aristotle and Plato considered aristocracy to be the best type of governance The term came into prominence in the context of ancient Greece where a class of eminent citizens was deemed best qualified to rule the peopleIn the various city states across ancient Greece, including tyranny, monarchy, oligarchy, aristocracy and democracy An attempt has been made to sort these forms of government according to how harsh they were on the population in general but like ice cream, each of these forms comes in different flavors (Me, 16)



An Aristocrat In Ancient Greece Series Book Ii Plato Theaetetus By Stathis Mylonas Audiobook Audible Com
/croesus-shows-solon-his-treasures-814443894-5aaff0f60e23d9003773c644.jpg)


Solon S Reforms And The Rise Of Democracy In Athens
Politics developed because of the polis and was ruled by the aristocracy How did the physical geography of Greece encourage the development of the citystate?Ancient Greece The term Ancient, or Archaic, Greece refers to the years BC, not the Classical Age ( BC) known for its art, architecture and philosophyThe aristocracy were wealthy because they owned large plots of land What effects did colonization have on mainland Greece?
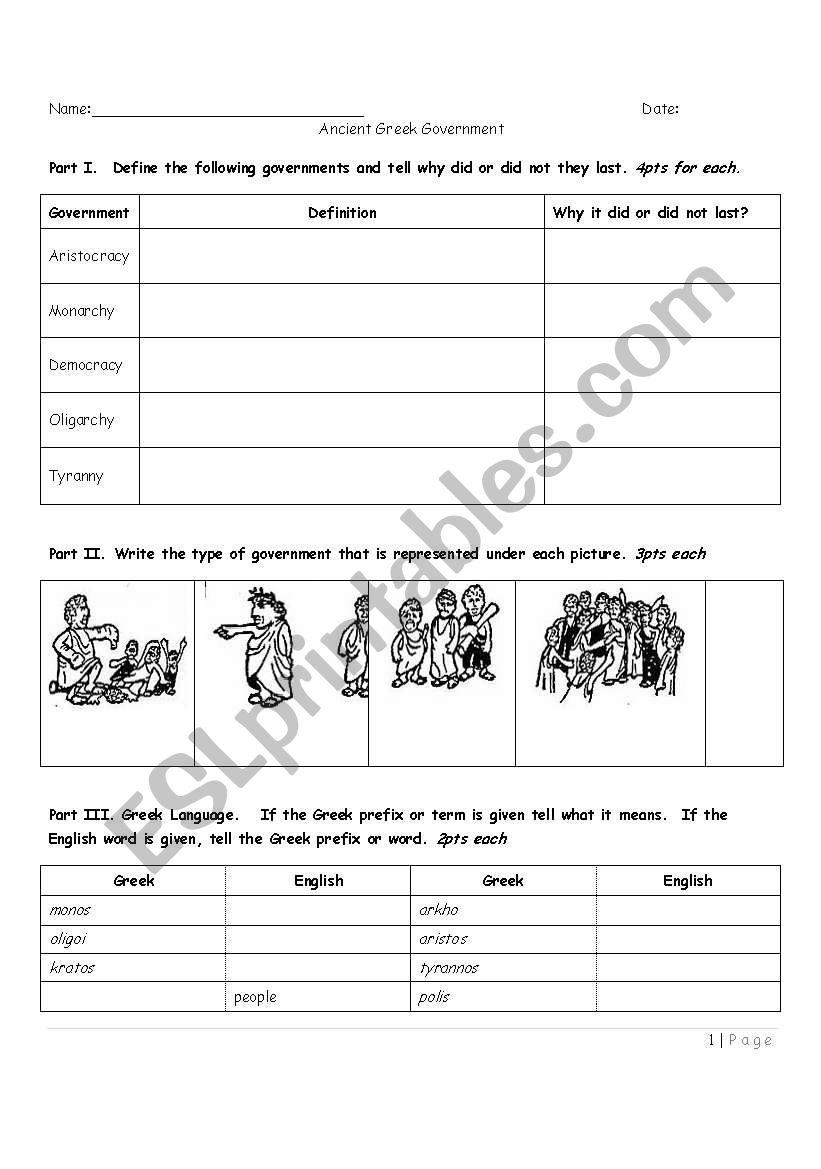


Ancient Greece Government Test Esl Worksheet By Small112


6 4 2 Trace The Transition From Tyranny And Oligarchy To Early Democratic Forms Of Government And Back To Dictatorship In Ancient Greece Including The Significance Of The Invention Of The Idea Of Citizenship
Ancient Greek politics, philosophy, art and scientific achievements greatly influenced Western civilizations today One example of their legacy is the Olympic Games Use the videos, media, reference materials, and other resources in this collection to teach about ancient Greece, its role in modernday democracy, and civic engagementAs conceived by the Greek philosopher Aristotle (384–322 bce), aristocracy means the rule of the few—the morally and intellectually superior—governing in the interest of allThe aristocracy is a social class that a particular society considers its highest order In many states, the aristocracy included the upper class of people with hereditary rank and titles In some, such as ancient Greece, Rome, or India, aristocratic status came from belonging to a military caste It has also been common, notably in African societies, for aristocrats to belong to priestly dynasties Aristocratic status can involve feudal or legal privileges They are usually below only the monar


Www Wsfcs K12 Nc Us Cms Lib Nc Centricity Domain 6742 The rise of democracy powerpoint pdf Pdf
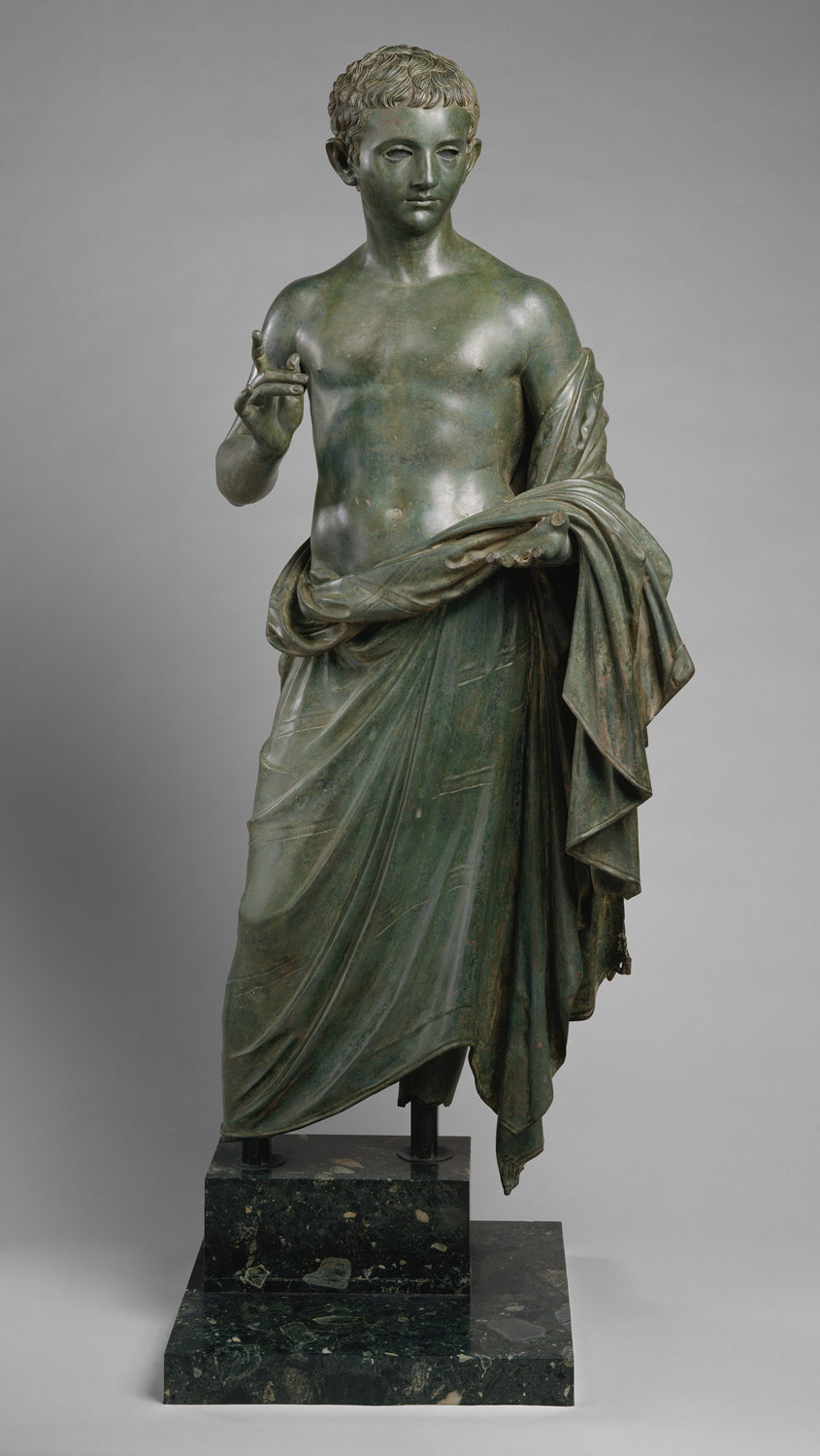



Ancient Greece 1 500 A D Chronology Heilbrunn Timeline Of Art History The Metropolitan Museum Of Art
Different types of birds were favored as pets in ancient Greece The Mynah bird was quite common pet among the aristocracy and often received special care Parakeets were also keptIn Ancient Greece it was used to describe the rule of the most qualified or the best citizens It was used by philosophers such as Aristotle or Plato, described, as said, as the rule of the most qualified, system which was favorably compared with Monarchy, the rule of the one In this hypothetical Aristocratic system hereditary rule would be forbidden and would only be allowed in case the children of the former Aristocrats performed in a way worth giving them this roleAn Ancient Greek Aristocracy is a form of government in which the bestqualified citizens rule The term was derived from the Greek word aristocrat, meaning "rule of the best" The concept evolved in Ancient Greece, whereby a council of famous citizens was commonly used and contrasted with "direct monarchy" in which an individual king held the power



Aristocracy And Athletics In Archaic And Classical Greece Nicholson Nigel Amazon Com Books


Ancient Greek Aristocracy Aristocracy Council Of Famous Citizens
The effects of colonization on mainland Greece included decreased population in the mainland but they still traded with each otherWhen the democracy in the ancient Greece fell, people began to seek another form of government They chose aristocracy Find out ancient Greek government facts here Facts about Aristocracy 4 the ancient Rome In the ancient Rome, aristocracy was also upheld The privileged citizens were gathered in a senate, consuls and a tribal assemblyWhat is Aristocracy Aristocracy is derived from the Latin terms aristokratía meaning the rule of the best As its etymology suggests, the concept of aristocracy first appeared in ancient Greece, and it referred to the rule by the bestqualified citizens Aristocracy was a favorable form of governance compared to monarchy



Interesting Facts About Ancient Greece And Its Government Brighthub Education



Were Blue Eyes And Blonde Hair Common Among Ancient Greek Aristocrats Page 1 Blonde Hair Hair Blue Eyes
Oligarchy is defined as the type of government where the rule of the government is in the hands of a few The word comes from the Greek terms oligos (meaning a few) and arkhein (meaning to rule) Around BCE, a small group of people started to share power and rule in a couple of Greek citystatesThe aristocracy is a social class that a particular society considers its highest order In many states, the aristocracy included the upper class of people with hereditary rank and titles In some, such as ancient Greece, Rome, or India, aristocratic status came from belonging to a military caste It has also been common, notably in African societies, for aristocrats to belong to priestly dynasties Aristocratic status can involve feudal or legal privileges They are usually below only the monar



Racial Type Of The Ancient Greeks A Racial Analysis Of The Ancient Hellenes Ghd



Heroes Of Bronze Nikephoros And Aegeus Greco Persian Wars Hero Ancient Greece



The Aristocrats In Ancient Greece Youtube
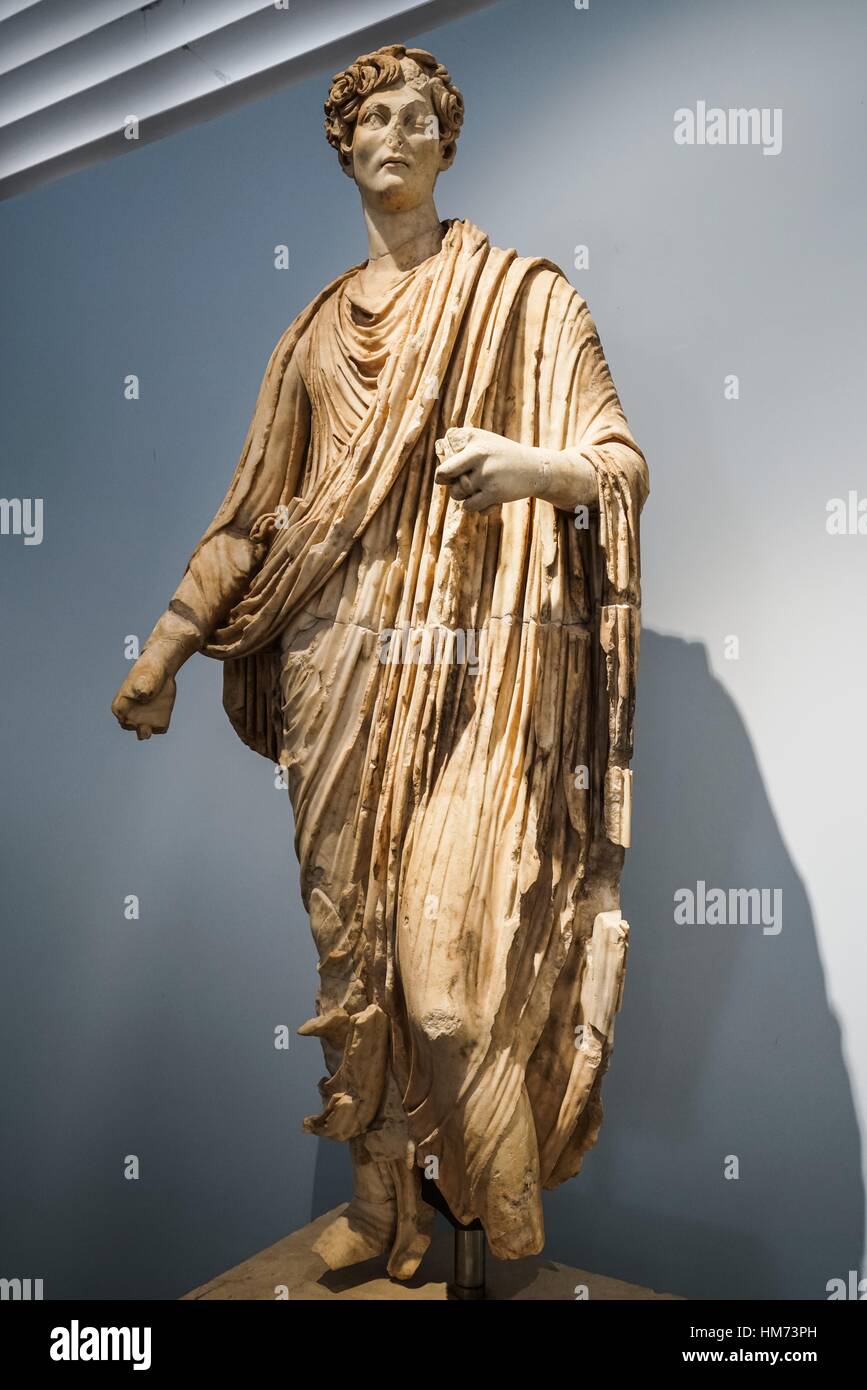



Young Aristocrat With Toga From Agora Aphrodisias Museum Ancient Stock Photo Alamy



Ancient Greece Social Class System Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Pedophilia In Ancient Greece And Rome Thecollector



What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Aristocracy



What Is Aristocracy Aristocracy


Aristocrats Rights And Responsibilities The Citizens Of Greece


Ancient Greece Legacies Hippocrates Aristotle Greek City State Of Olympia



Monarchy Aristocracy Tyranny Oligarchy And Democracy As Forms Of Government In Ancient Greek City States Steemit



Patricians Ancient Greece And Rome An Encyclopedia For Students 4 Volume Set



Ancient Greece Flashcards Quizlet



Ancient Greek Government World History Encyclopedia



Greek Wh1 Project By Mkwarlick On Emaze



Clothing In Ancient Greece Wikipedia



Draco S Law Code In Ancient Athens Brewminate



Peisistratus Biography Legacy Facts Britannica



Greek Illusion Perfectionist



Ancient Greece History



The Ancient Greek Blonde Aristoi Egyptsearch Forums


Difference Between Aristocracy And Oligarchy Definition Origin Type Of Government



Aristocracy Class Wikipedia
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Ancient-Greece-58e267583df78c5162b0e50f.jpg)


Comparing Ancient Greece And Ancient Rome



How Ancient Greek And Roman Art Became The Ideal Model By Christopher P Jones Thinksheet Medium


3



Ancient Greek Society World History Encyclopedia



Elections Were Never Part Of The First Democracy In Ancient Greece They Viewed Elections As A System That Encourages Aristocracy And Elitism Has The U S Political System Become Too Geared To The



The Ideal Ancient Greek Politics Steemit



Tin Soldiers Museum Top Spartan Aristocrat 90 Mm Ancient Greece Ebay


Birth Of Democracy The Athenian Aristocracy


Ancient Greece Storyboard Por Gabby Linetsky


Ancient Greece Women 1 Ancient Greece Facts Com


Government In Ancient Greece Facts And Details



Kouroi Part 4



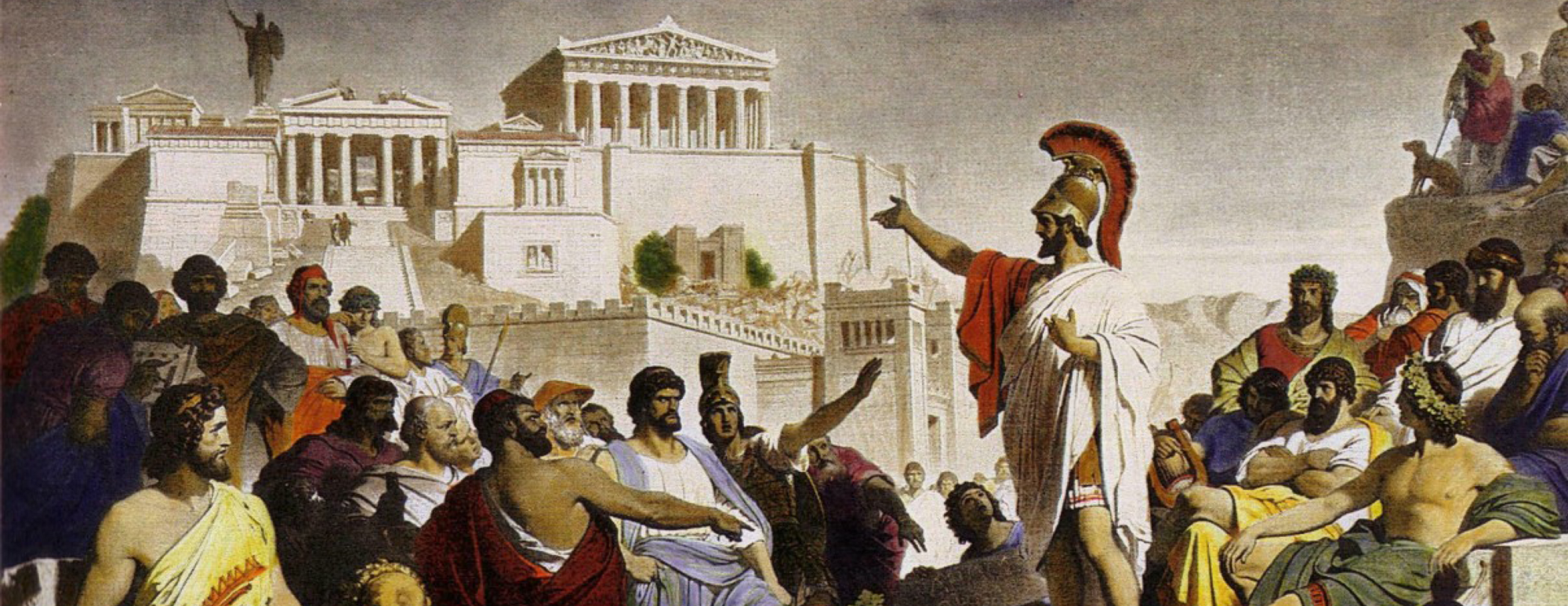
The Life And Rule Of Pericles Brewminate



7 Incredible Ancient Greek Vase Paintings To Marvel At



Welcome To Ancient Greece



Ancient Greek Democracy History



Ancient Greece And Its Government By James Gutierrez



Ancient Greek Funeral And Burial Practices Wikipedia



Athenian Democracy Ancient Greece Ppt Download



Ancient Greece 6th Grade Ppt Video Online Download


Ancient Greece Men2 4 Ancient Greece Facts Com


Weapons Control In Ancient Greece When An Accident Was Deadly Ancient Origins


Ancient Greece Government Storyboard By Amyagurto



Kouroi Part 4



Ancient Greece Goverment Sutori


How Aristocratic Government Works



Amazon Com Aristocracy In Antiquity Redefining Greek And Roman Elites Kataloge Und Schriften Der Staatlichen Bibliothek Regensburg Fisher Nick Fisher Nick Van Wees Hans Books



Tyrant Definition Facts Britannica


Birth Of Democracy The Athenian Aristocracy



Monarchy Aristocracy Tyranny Oligarchy And Democracy As Forms Of Government In Ancient Greek City States Steemit



Ancient Greek Aristocracy Bing Images Mesopotamia Historical Costume Ancient History



Social Class In Ancient Rome Wikipedia



Ancient Greek Aristocracy Bing Images Ancient World History Athens Portrait



The Top Benevolent And Malevolent Dictators From History



Power And Fate The Aristocrats In The Iliad Classical Wisdom Weekly



Racial Type Of The Ancient Greeks A Racial Analysis Of The Ancient Hellenes Ghd



Aristocracy Definition Examples Facts Britannica


Kirstengreekliterature Licensed For Non Commercial Use Only Government And Politics



Ancient Greece Democracy Flashcards Quizlet



Ancient Greek Aristocracy Bing Images Ancient Image Ancient Greek
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/-leonidas-at-thermopylae---5th-century-bc---c1814---artist--jacques-louis-david-463927039-5bfd8f23c9e77c0051c0d1ed.jpg)


7 Points To Know About Ancient Greek Government
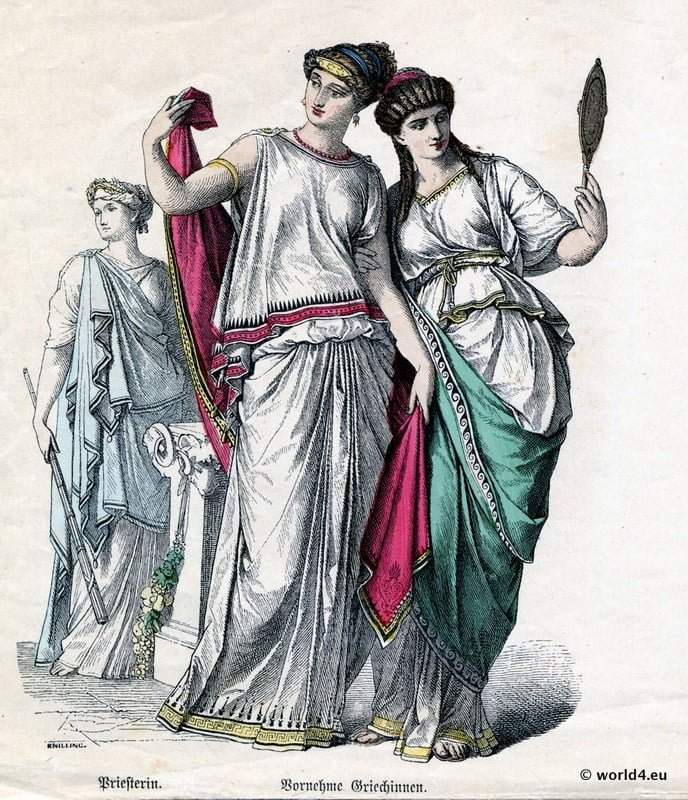



Ancient Greek Priestess And Nobility Chiton With Kolpos


3


Introduction Ancient Greece



Top 12 Greatest Leaders In Ancient Greece Ancient History Lists



Ancient Greece Principles Of Public Speaking



The Structure Of State Power Of Ancient Greece Features Of Management And Development Of Managerial Thought In Ancient Greece Local Government Development


Ancient Greece Declassified Podcast



The Rise Of Democracy In Ancient Greece Ppt Video Online Download



Ancient Greek Democracy History


Ancient Greece Storyboard Storyboard By Kwayla



Alcmaeonid Family Aristocrats Of Ancient Greece


Q Tbn And9gcro4tabqqrkub2iawyhuuzq9b1llvdz1ltby Nvruyq 6d8gp8n Usqp Cau


コメント
コメントを投稿